We continue the focus on Myeloma kidney, which started last month with Light Chain Cast Nephropathy. This month the emphasis is on Light Chain Proximal Tubulopathy with Crystals (LCPT)- a distinct entity.
Terminology
- Chronic tubulointerstitial nephropathy caused by intracytoplasmic crystalline inclusions
- Composed of monoclonal light chains present in proximal tubular epithelial cells
Pathogenesis
- Abnormal monoclonal immunoglobulin light chains (usually kappa, Vk1)
- Produced by clonal proliferation of plasma cells
- Resistant to enzymatic breakdown
Clinical Issues
Incidence
Rare (~ 0.06% of renal biopsies) but may be overlooked
Fanconi syndrome (acquired)
- Normoglycemic glycosuria
- Aminoaciduria, uricosuria
- Hyperphosphaturia with hypophosphatemia
- Chronic renal failure, slowly progressive
Histology
- Glomeruli: normal
- Tubules: intracellular crystalline inclusions within proximal tubular epithelial cells
- Acute and chronic tubular injury
- May show other manifestations of monoclonal protein deposition
– Crystal-storing histiocytosis with monoclonal light chains
– Myeloma cast nephropathy
– Light chain deposition disease (in GBM and TBM)
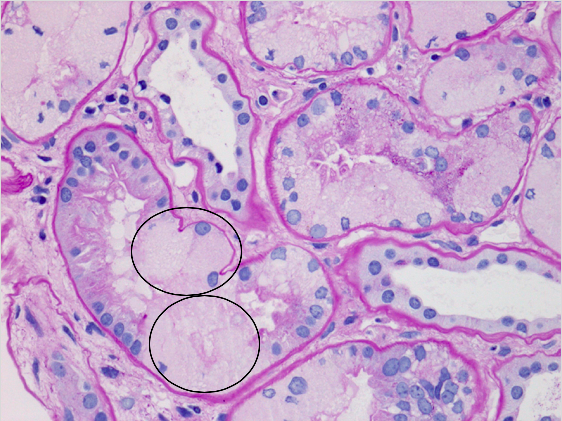
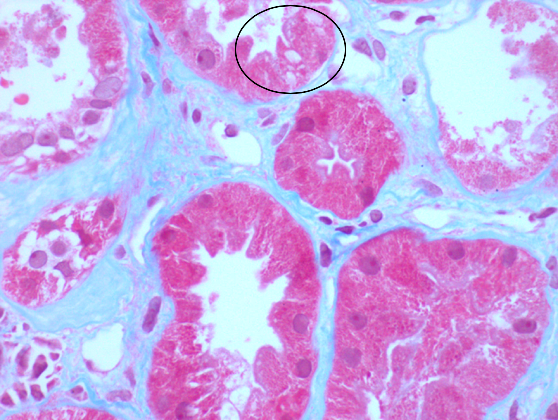
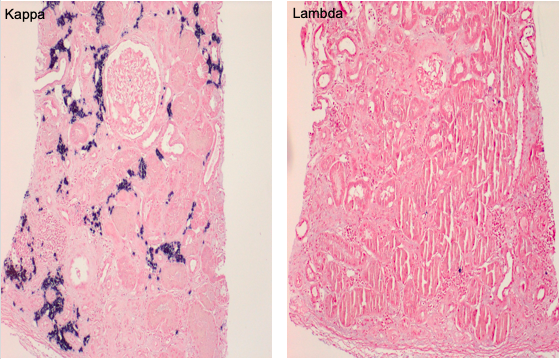
Figure 3: Kappa-light chain restricted atypical plasma cell infiltrate (in situ hybridization)
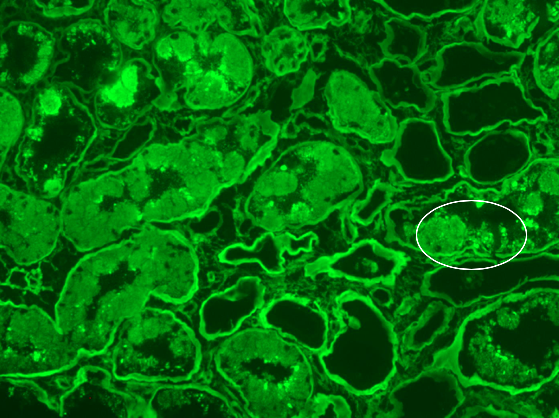
Immunofluorescence (IF)
- Intracellular monotypic staining for κ or λ light chain
- IF can often be negative in crystalline monogammopathy, and staining of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue using IHC or pronase IF is recommended to demonstrate monotypic light chain
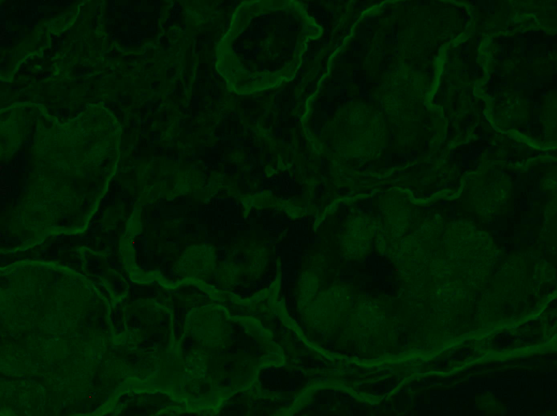
Electron Microscopy
Electron-dense crystalline structures within cytoplasm of proximal tubular epithelial cells
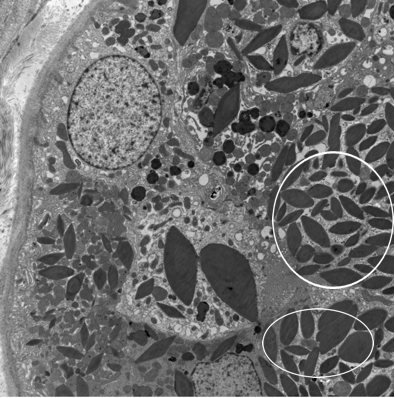
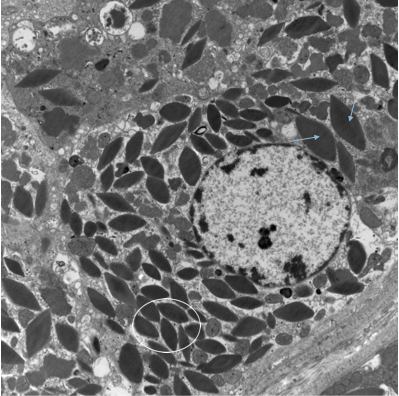
Serologic Testing
- Monoclonal protein in serum, usually IgG kappa
- Bence Jones proteinuria, usually kappa light chain
Treatment
Treatment of underlying plasma cell dyscrasia or lymphoma
Tiffany Shao, MD FRCPC FCAP
University of Calgary, Canada


