ASN Board Review Course & Update: Register by 6/20 for Discounted Rate!
Kidney Comics: T-Cell Mediated Rejection (Kidney Transplant)
Skeleton Key Group Case #33: Atrocious Acidosis
Origins of Renal Physiology Course: Fellows 2024
2024 NephMadness Tournament Challenge: Bracket Submissions Due March 31st!
Continuous renal replacement therapy Education Module
Applications open for the WIN Fellow School for Leadership Education
American Transplant Congress 2024: Medical Student & Resident Travel Grant Applications Due 3/11
High Output Cardiac Failure and Pulmonary Hypertension in Kidney Transplant Recipients
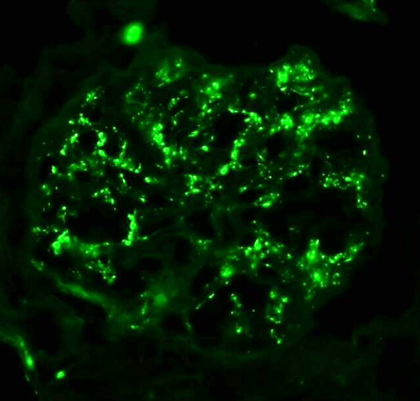
Kidney Biopsy of the Month: Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis
Definition A group of podocytopathies (of varying etiologies) share a common morphologic feature of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS), typically with moderate to heavy proteinuria. The term “sclerosis” means healing and it is characterized by accumulation of glomerular collagen…
Kidney Biopsy of the Month: BK virus nephropathy
In 1971, a group of virologists in London first described a novel polyomavirus they discovered in the urine and urothelial cells of a kidney transplant recipient who had developed ureteric stenosis. Named after the patient it was first…
Kidney Biopsy of the Month: Thrombotic Microangiopathy
Thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA) is characterized by microvascular endothelial injury and thrombosis, presenting both clinically and histopathologically in two main forms; acute and chronic TMA. Etiology and Clinical Presentation Table 1: Etiologies of TMA classified according to clinical presentation…
Kidney Biopsy of the Month: Amyloidosis
Amyloidoses are a group of diseases resulting from deposition of amyloid, insoluble fibrils derived from various precursor proteins, into extracellular tissues. Amyloidoses are acquired or hereditary, and depending on where amyloid deposits, can affect a wide range of…
Kidney Biopsy of the Month: Lupus Nephritis
Our last post on lupus nephritis focused on pathogenesis ,clinical presentation, grading and class I/II disease. The next segment this month will cover class III-VI disease. Class III: Focal lupus nephritis It accounts for about 9-24% of lupus…
Kidney Biopsy of the Month: Lupus Nephritis
Our endeavor for the next 2 months will be a focus on Lupus nephritis. This month we will cover general aspects of disease, introduction to subclasses and activity indexes. Background and Demographics Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a…
Kidney Biopsy of the Month: Membranous Nephropathy
Demographics Membranous nephropathy (MN) is one of the most common causes of nephrotic syndrome in Caucasian adults above 40 years. However, it can occur in different ages and ethnicities. The incidence was estimated about 8-10 cases per one…
Kidney Biopsy of the Month: Atheroembolic Kidney Disease
Introduction Atheroembolic kidney disease develops due to occlusion of small renal arteries by cholesterol crystal emboli originating from the rupture of atheromatous aortic plaques. It is part of a systemic disease and embolization often affects other organs such…
Kidney Biopsy of the Month: C3 Glomerulonephritis
Our focus on myeloma related disorders continues- view previous posts here. Pathogenesis C3GN is a type of glomerulonephritis characterized by dominant C3 deposition resulting from overactivation of the alternative pathway of complement (APC) from acquired or hereditary causes. The…
Kidney Biopsy of the Month: Proliferative Glomerulonephritis with Monoclonal IgG Deposition
Our focus on myeloma related disorders continues- view previous posts here. Pathogenesis Proliferative glomerulonephritis with monoclonal immunoglobulin deposition (PGNMID) is seen in less than 1% of native kidneys and is due to IgG kappa (IgG3 most commonly) deposition in…