2024 NephMadness Tournament Challenge: Bracket Submissions Due March 31st!
Continuous renal replacement therapy Education Module
Applications open for the WIN Fellow School for Leadership Education
American Transplant Congress 2024: Medical Student & Resident Travel Grant Applications Due 3/11
High Output Cardiac Failure and Pulmonary Hypertension in Kidney Transplant Recipients
The first annual NephMadness Invitation Tournament (NIT) is coming to the National Kidney Foundation 2024 Spring Clinical Meeting (SCM) in Long Beach, CA!
Skeleton Key Group Case #32: Hitting the Reset Button on Hyponatremia
2024 NephSIM Nephrons: Applications Due 11/15
Skeleton Key Case #31: Paralyzing Potassium
Urine Sediment of the Month: Bacterial Variant Forms
Urinary tract infections (UTI) are among the most common medical disorders in the world. Bacteria are the main infectious agent that causes UTIs, and bacteriuria and leukocyturia are the hallmarks of urinary sediment in patients with UTI. Bacteria…
Urine Sediment of the Month: Findings in Cirrhosis, Cholestasis, and Hyperbilirubinuria
Microscopic examination of the urinary sediment in the context of hyperbilirubinemia and increased urinary bilirubin excretion requires special attention to the unique chromatic characteristics acquired by the specimens. As serum bilirubin increases, a yellow-tinged urine becomes increasingly noticeable….
Urine Sediment of the Month: 4 Flavors of Nucleated Cells
In the routine urinary sediment examination, you may come across 4 types of nucleated cells: 1. Squamous epithelial cells2. Leukocytes3. Transitional epithelial cells4. Tubular epithelial cells Let’s discuss how to differentiate between them. Squamous epithelial cells are easily…
Urine Sediment of the Month: All About Those Oval Fat Bodies
Damage to the glomerular basement membrane allows plasma lipids to enter the urinary space. These lipids may appear in various forms, either as free lipid droplets, lipid casts, oval fat bodies, and/or as cholesterol crystals. In most cases,…
Urine Sediment of the Month: Drugs & Crystalluria
Several drugs, mainly antimicrobial or antiviral agents, can cause transient crystalluria, in isolation or in conjunction with other urinary abnormalities and a wide range of clinical implications. The factors favoring the formation of drug crystals are drug overdose,…
Urine Sediment of the Month: Dysmorphic Red Blood Cells, Blebs, & Spikes
Urine acanthocytes are a distinct type of dysmorphic erythrocytes that can be found during microscopic examination of the urinary sediment. Their unique characteristics make them rather pathognomonic of hematuria that originates from a glomerular disease, i.e., glomerular hematuria…
Urine Sediment of the Month: Cystine Crystals
Cystinuria is the most common kidney stone disease with Mendelian genetics. Caused by mutations in SLC7A9 and SLC3A1, affected patients excrete high amounts of cystine in their urine and are vexed by recurrent episodes of nephrolithiasis. Cystine stones…
Urine Sediment of the Month: A Case of Recurrent “Sinus Infections,” Pyuria, & Hematuria
This is a fictional case, designed for educational purposes The Case The patient is a 66 year-old with a history of hypertension who presented with complaints of fatigue and recurrent “sinus infections” over the past few months. He…
Urine Sediment of the Month: Pigmented Casts & What Those Pretty Colors Tell Us
Eric Bywaters was the first to use the nomenclature “pigmented casts” in a 1941 British Medical Journal publication about crush syndrome where he illustrates pigmented casts (due to myoglobin) with a photomicrograph (Figure 1) of the kidney biopsy…
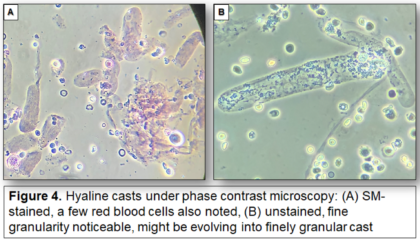
Urine Sediment of the Month: Colorless, Transparent Hyaline Casts
Hyaline casts are traditionally known to lack clinical significance. However, because they are frequently found during urinary sediment microscopy, hyaline casts should be correctly identified and distinguished from other types of casts. They are colorless transparent cylindrical structures…